Automobiles, aircraft parts, medical implants. The ability to manufacture lighter, quicker, waste-free parts on demand has revolutionized the production of Industry 4.0. Faced with the need to change the rules of the game, additive manufacturing has become one of the foundations of the new industry. And metal 3D printing is one of its many possibilities.
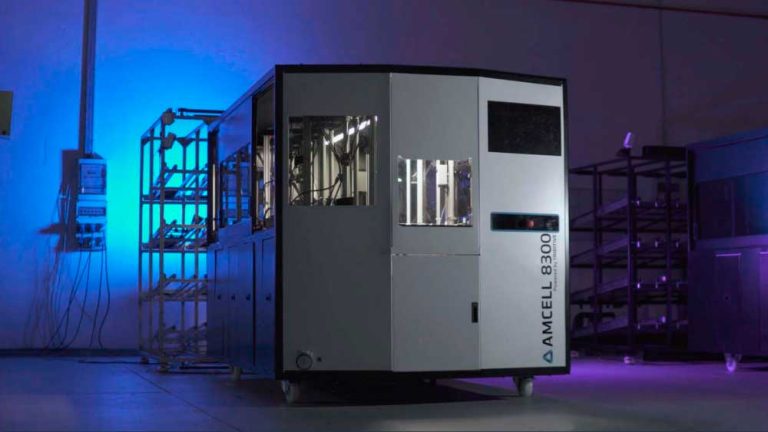
There are numerous polymer additive manufacturing machines. The same goes for metal. In response to industry demand, many companies have decided to offer this service to the aeronautics, medical, automotive and other sectors. However, few have machines capable of printing simultaneously on both materials. To do this, Triditive, a pioneer company in automated additive manufacturing in Spain, developed the Amcell 8300, the first and only platform capable of producing parts with both metals and polymers.
How metal 3D printing works
Through metal filament – plastic filament with metal particles-, the machine is capable of manufacturing complex parts quickly, reducing waste, energy consumption and manufacturing cost. This metal production model makes it possible to obtain parts that are up to 60% lighter and more resistant.
This technology is based on sintering, which is the application of high temperatures to a produced part, without reaching the melting point, so that it is compacted and creates a solid piece. The metal particles are joined and distributed to create the desired shape.
What metals are used for 3D printing
Depending on the technology and the desired part, the machines can work with one material or another, but the list is long: stainless steel, bronze, aluminum, nickel, titanium, gold and inconel, among others.
Stainless steel
Due to its good resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, stainless steel is frequently used for printing tools, molds, kitchen equipment and engine parts.
More standard versions can be used, such as DIN 1.4404, X 2 CrNiMo 17 13 2, AISI 316L, UNS S31603; or 17-4 PH stainless steel, characterized by its high elastic limit, its good resistance to corrosion and its high resistance to wear.
Titanium
Thanks to its properties, it is used for light structures with high requirements, in applications where the performance of the piece prevails over its cost. Along with the reduction of waste in the additive manufacturing model, titanium has become another of the most used materials for 3D printing, since its use has become more profitable.
Inconel
It is a nickel superalloy that offers great thermal resistance (55% nickel and 21% iron). It can maintain its structural properties up to 650ºC. Thanks to its characteristics, it is used in sectors associated with extreme temperature conditions: turbines, heat exchangers, engines or cryogenic devices.
Metal 3D printing methods
There are three methods for metal printing: direct deposition, powder bed
fusion, and binder jetting.
Direct deposition method
It consists of sending a certain amount of powdered metal through a nozzle. The metallic powder shoots out in the form of a beam. When hit by a laser, the particles fuse together and become solid upon reaching the point of deposition.
Binder injection method
In this method, metal powder is combined with sand and ceramic powder. During the process, a liquid bonding resin is placed on top of the powder. The resin solidifies the powder particles to build the desired object.
Powder bed fusion method
It is very similar to the binder injection method, but instead of using resin to bond the particles, it uses a high-temperature laser or electron beam. The laser heats the metal powder and fuses its particles, creating a stable solid layer.
This method can be made through different techniques, such as selective laser sintering, direct metal laser sintering, selective laser melting, and electron beam melting.
Advantages and disadvantages of metal 3D printing
Like any technology, metal 3D printing has its pros and cons:
Advantages
- This process is used to manufacture complex, custom, and on-demand parts.
- Metal printed parts can be optimized to increase their performance, as well as to minimize their weight and the number of components required for their assembly.
- This type of printing allows you to create pieces within others. Thus, engineers can design a complex set of parts in a single print.
- Complex tools and programming are avoided, which reduces the cost compared to traditional models, such as machining or casting.
Disadvantages
- The cost of the material and its manufacture are high.
- Metal 3D printing systems require very precise manufacturing conditions and process control, hence their build volume is limited.
- Some designs may not be suitable for metal 3D printing and need to be modified.
Conclusion
The benefits of metal 3D printing in sectors such as aeronautics and the industrial sector itself are remarkable. In addition to these reasons, its success lies in its commitment to sustainability and local production, at a time when they are more necessary than ever.









